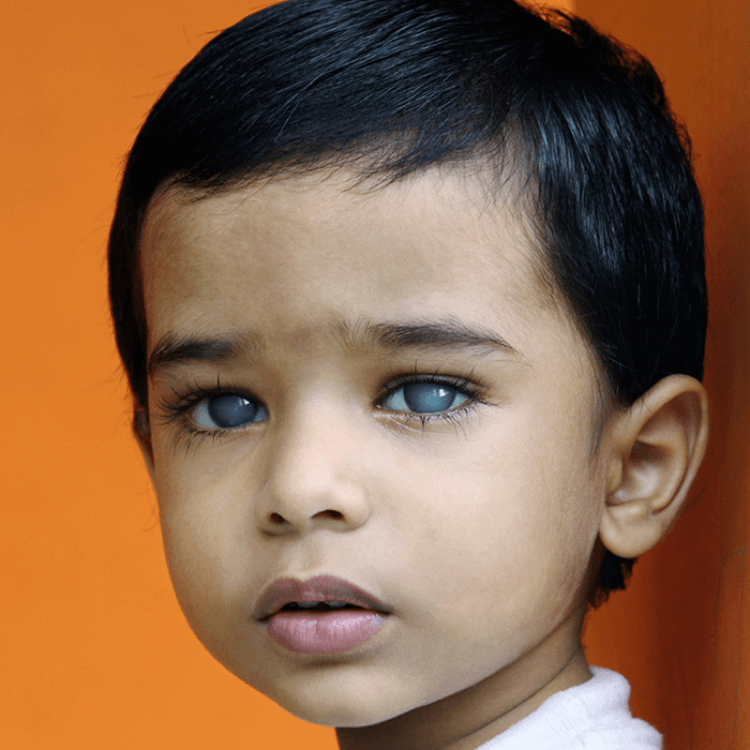
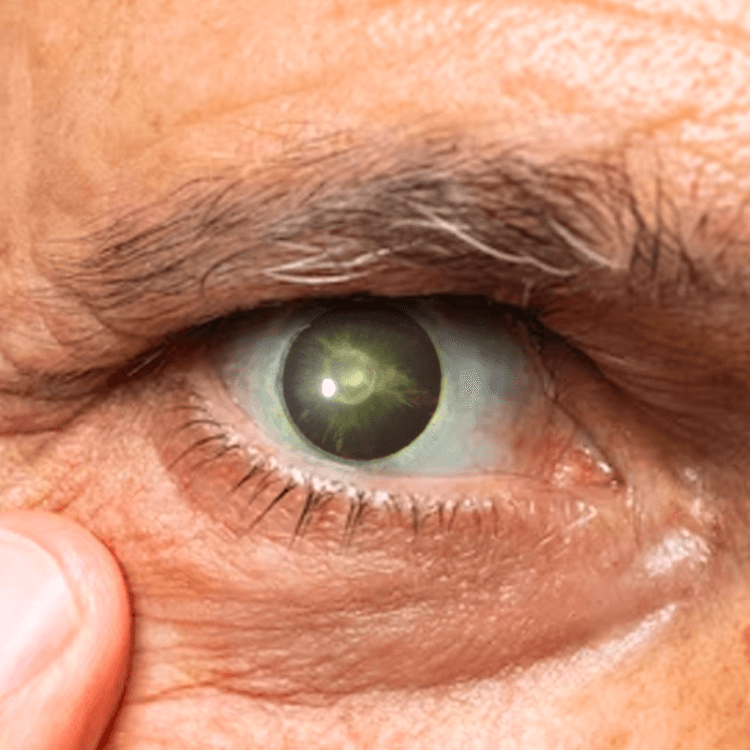
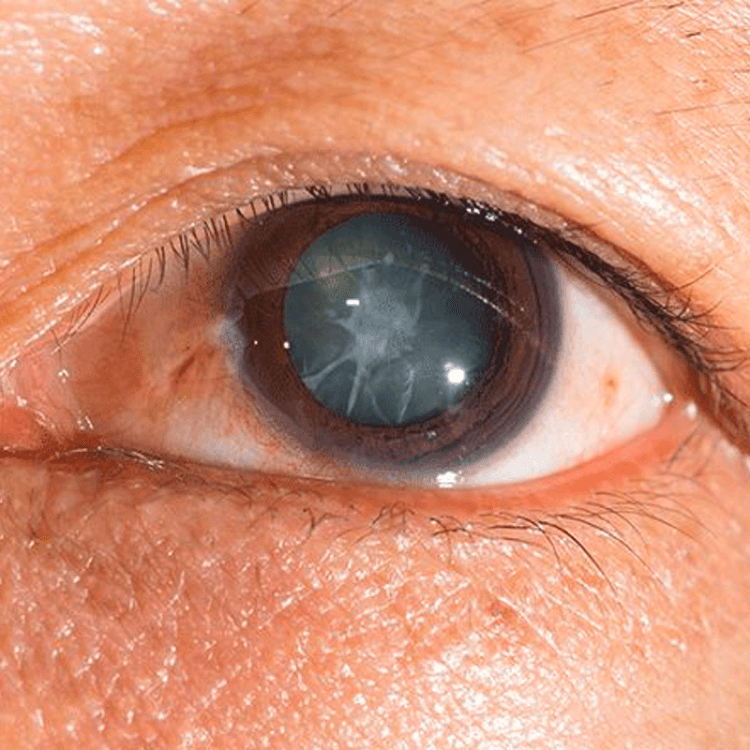
Cataract
Cataracts occur when the eye's natural lens becomes cloudy, causing vision to blur like looking through a foggy or dusty car windshield.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that affect the optic nerve after elevated eye pressure which may cause blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy happens when high blood sugar levels damage the retinal blood vessels. In the early stages of Diabetic Retinopathy, symptoms may not be noticeable.
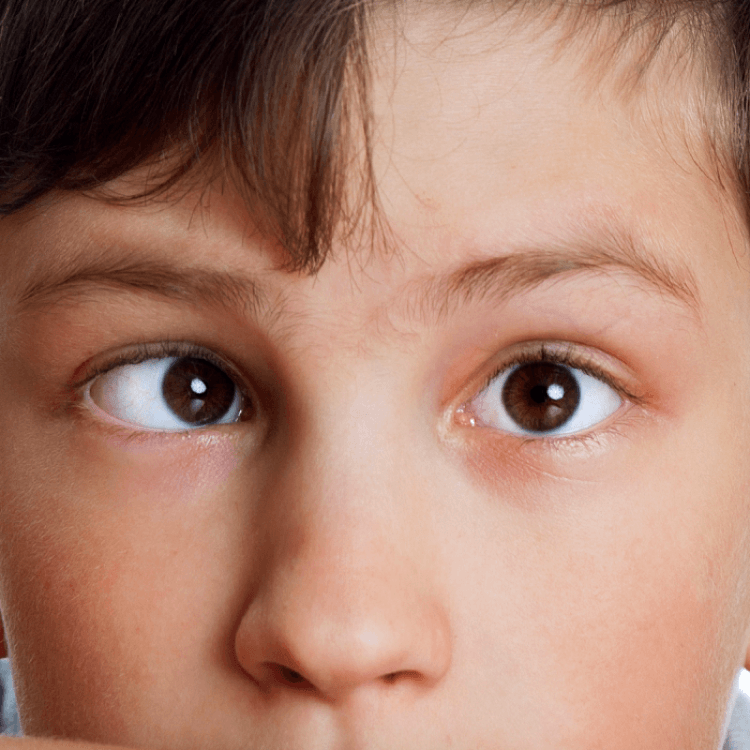
Squint
Squint is a disorder in which the eyes don't look in exactly the same direction at the same time. It is also known as ‘Strabismus’ or ‘Cross eyed’.
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Detachment occurs when the retina separates from its supporting tissue, leading to severe vision loss and blindness.
Retinopathy Prematurity
Retinopathy Prematurity (ROP) is an eye condition occurring in premature infants, where abnormal blood vessels grow in the retina, potentially resulting in blindness.
Macular Hole
The macula is the centre of your retina, the thin layer at the back of your eye. A macular hole is when a circular opening forms in this macula.
Traumatic Cataract
Traumatic Cataract is the clouding of the lens due to eye trauma, either blunt or penetrative, which damages the lens fibres.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract
Posterior Subcapsular is a type of cataract that begins as a small spot near the back of the lens and causes glare and halos around lights at night.
Congenital Glaucoma
Congenital Glaucoma is a rare genetic eye condition that affects children at birth causing abnormally high eye pressure.
Rosette Cataract
Rosette Cataract is a form of traumatic cataract caused by either blunt force trauma or penetrating eye injury.
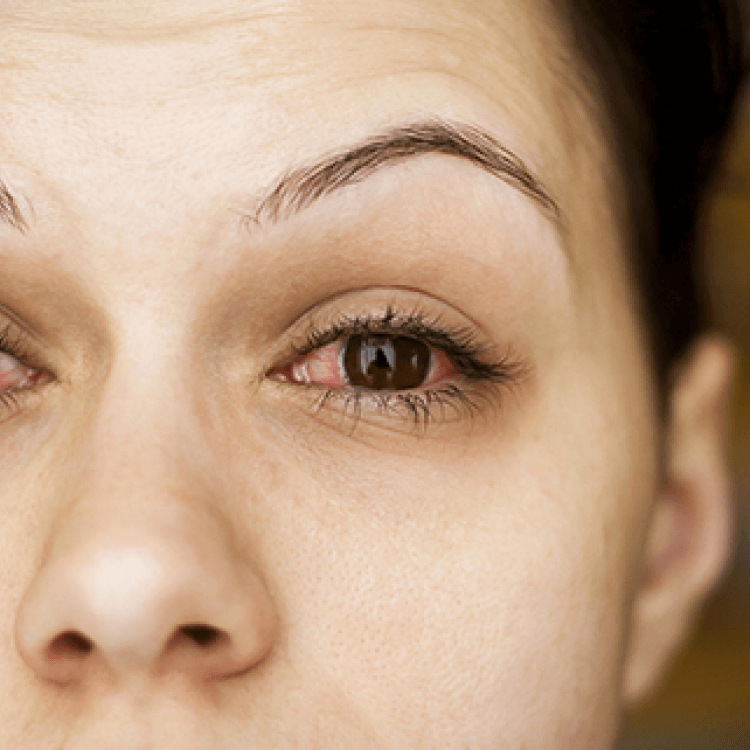
Uveitis
Uveitis refers to eye inflammation that affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall. It can affect one or both eyes.
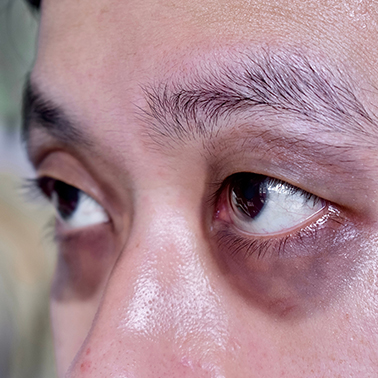
Orbital Trauma
Ocular or orbital injuries might cause pain around the eye, bruising, swelling, bleeding from cuts, facial numbness, and vision changes.