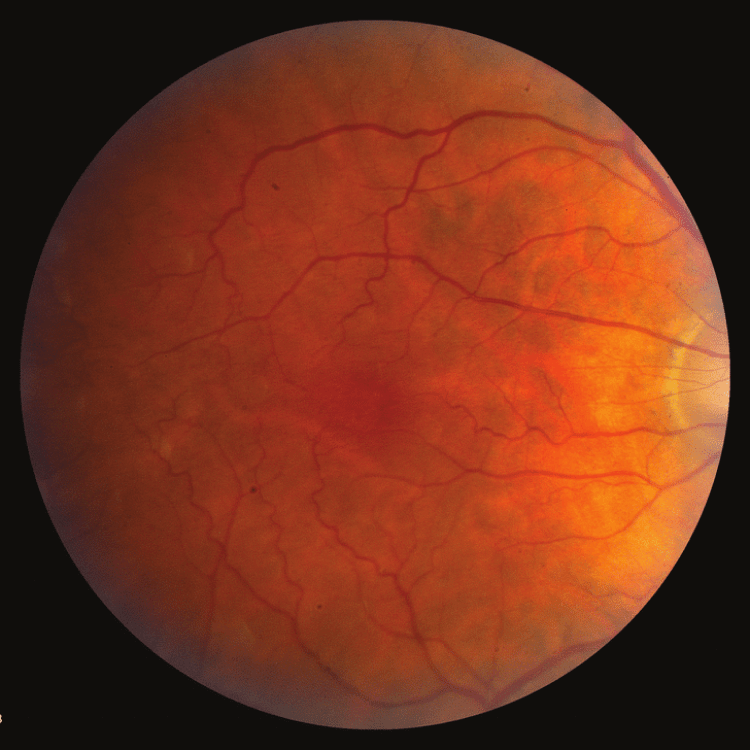
Diabetic Retinopathy
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy happens when high blood sugar levels damage the retinal blood vessels.
There are 2 types of Diabetic Retinopathy:
1. Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
In NPDR, the walls of the retinal blood vessels are weakened, leading to leakage from them and subsequent retinal swelling.
2. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
A more severe form develops when damaged blood vessels become blocked, leading to the growth of new abnormal blood vessels, which are very fragile and tend to bleed causing haemorrhage. These new vessels and proliferations can contract and lead to tractional retinal detachments (TRD). Both these events lead to severe vision loss.
Symptoms
Symptoms to look out for
In the early stages of Diabetic Retinopathy, symptoms may not be noticeable. As the condition progresses, symptoms may include:


Fluctuating vision

Dark spots or strings(floaters)

Distorted vision

Poor vision at night

Partial or total loss of vision
Risk Factors
Who is at risk of getting Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatments Available
Here’s how our experts treat it
Treatment options for Diabetic Retinopathy vary depending on severity and stage. At Vasan, after a thorough diagnosis, we employ the perfect treatment for you such as:
Control Blood Sugar Levels
Managing Diabetic Retinopathy involves controlling blood sugar levels. This includes lifestyle changes like exercise and a healthy diet, along with medications such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
Laser Therapy
Also called Photocoagulation, it involves using a laser beam to seal leaking blood vessels and inhibit the growth of new ones, helping to prevent further damage to the retina and slow disease progression.
Anti-VEGF Agents
Anti-VEGF agents are a group of medications which block the activity of VEGF, therefore reducing bleeding and vascular leakage.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is an advanced surgery done by our specialists to remove the gel-like substance called ‘vitreous humour’ from inside your eye. This helps them get better access to your retina.
Anti-inflammatory Medication
Anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs and corticosteroids reduce eye inflammation and prevent additional damage.
Intravitreal Implants
If anti-VEGF injections aren't suitable or ineffective, consider intravitreal implants. These tiny implants, containing dexamethasone are injected into your eye which reduces eye swelling and improves vision, without needing to be removed.
FAQs
Diabetic Retinopathy results from high blood sugar levels due to diabetes. Prolonged high sugar levels can harm the retina, which is responsible for detecting light and transmitting signals to the brain via the optic nerve.
Diabetic Retinopathy often starts without symptoms, but may later cause blurred vision, fluctuating vision, double vision, floaters, or impaired colour vision due to weakened blood vessel walls in the retina due to uncontrolled diabetes.
Diagnosis involves a thorough eye exam, including visual acuity, dilated eye check, eye pressure measurement, and sometimes imaging tests like optical coherence tomography (OCT) or fluorescein angiography.
Diabetic Retinopathy has 4 stages:
- Mild Non-proliferative Retinopathy:
- Early stage with microaneurysms (tiny swellings of blood vessels), often unnoticed but detectable clinically.
- Moderate Non-proliferative Retinopathy:
- Blood vessel weakening and leakage, leading to macular oedema (swelling causes too much fluid in the body) and potential vision loss.
- Severe Non-proliferative Retinopathy:
- Increased vessel blockage, haemorrhages, and fluid leakage deprive the retina of blood supply.
- Proliferative Retinopathy:
- Advanced stage with new fragile blood vessel growth, prone to rupturing and causing severe vision loss or blindness.
- While complete prevention may not be guaranteed, effectively managing diabetes can greatly reduce the risk or slow the progression of Diabetic Retinopathy.
While Diabetic Retinopathy damage is usually irreversible, early detection, proper diabetes management, and appropriate treatment can prevent further progression and preserve vision. Regular eye exams and timely intervention are key to effective management.
Other Diseases
Know more about other Eye Diseases
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Detachment occurs when the retina separates from its supporting tissue, leading to severe vision loss and blindness.
Retinopathy Prematurity
Retinopathy Prematurity (ROP) is an eye condition occurring in premature infants, where abnormal blood vessels grow in the retina, potentially resulting in blindness.