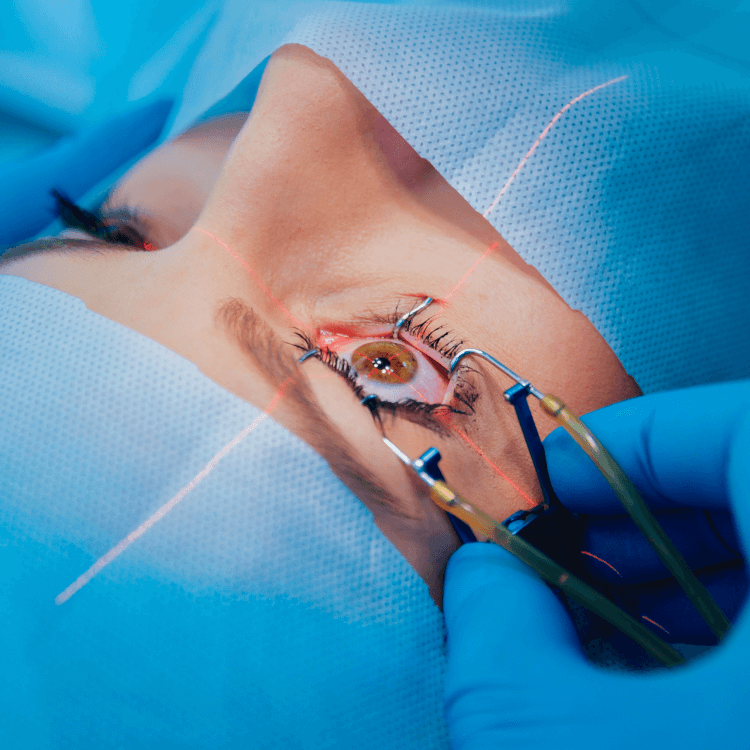
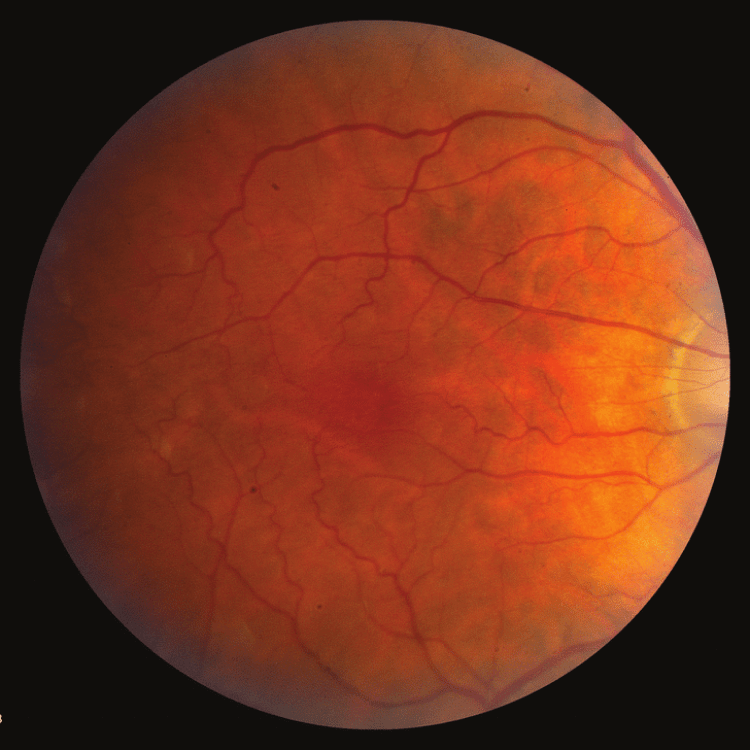
Retinal Detachment
What is Retinal Detachment?
Retinal Detachment occurs when the retina separates from its supporting tissue, leading to severe vision loss and blindness. It happens due to retinal tears, breaks, inflammation, or trauma and requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms
How to know if your Retina is detached
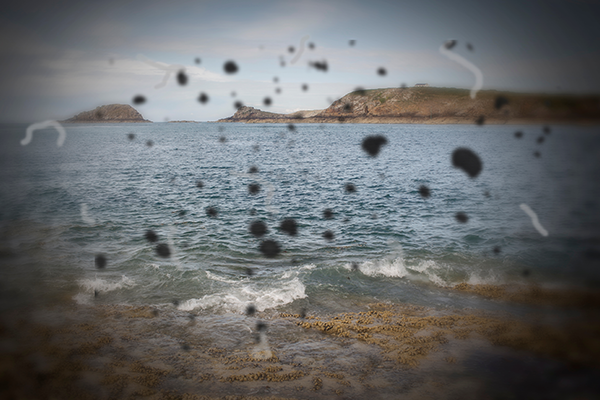


Sudden increase in floaters
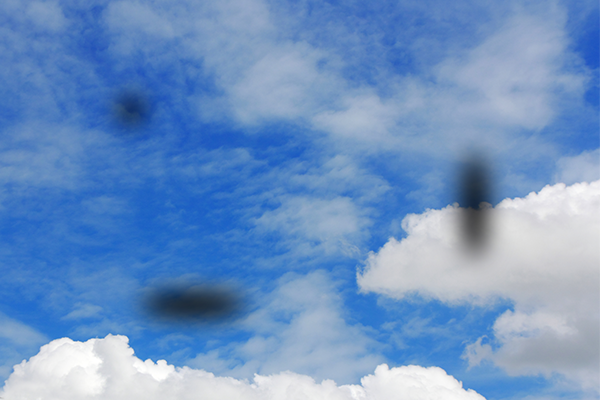

Ring of floaters
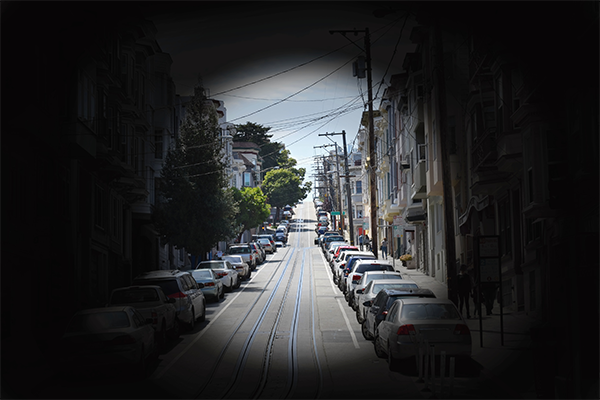

Sensation of veil-like or curtain over vision
Distorted vision
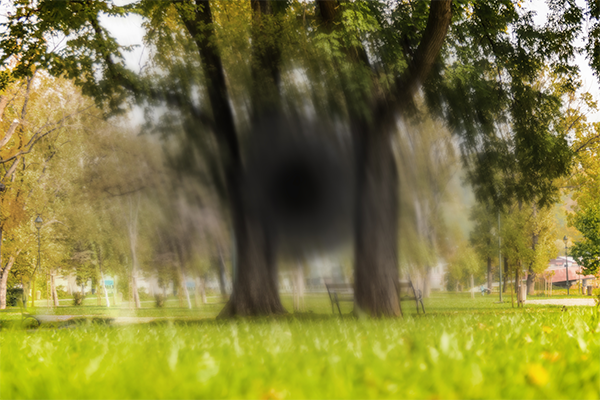

Central visual loss
Risk Factors
Common risk factors of Retinal Detachment
Treatments Available
Here’s how our experts treat it
At Vasan, once the diagnosis is made, the doctor recommends retinal surgeries depending on the type and severity of the detachment. The treatments include:
Retinal Laser Photocoagulation
Laser surgery seals or reattaches the retina by scarring the area around the detachment or tear.
Cryopexy
Cryopexy repairs retinal tears by applying intense cold therapy to the back of the eye using a specialised probe, which creates scar tissue around the tear.
Pneumatic Retinopexy
This process involves using gas or air bubble injection into the vitreous cavity that pushes against the retinal hole, stopping fluid flow and allowing the retina to reattach.
Scleral Buckling
Scleral buckling involves securing a piece of silicone band or sponge to the sclera, the white part of your eye. This action helps reattach the retina by pushing it back into its supportive tissues.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is an advanced surgery done by our specialists to remove the gel-like substance called ‘vitreous humour’ from inside your eye. This helps them get better access to your retina.
FAQs
There are many causes of Retinal Detachment, but the most common causes are pre-existing retinal weak areas, eye trauma/prior eye surgery, high myopia or ageing.
Yes. Retinal detachment surgery involves reattaching the retina to the back of the eye and sealing any breaks or holes. The treatment has a high success rate if treated in time.
Various tests to identify detached retinas in your eyes like:
- Dilated exams
- Ocular ultrasound
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Following a thorough evaluation, the doctor recommends suitable options for Retinal Detachment eye surgery.
Retinal Detachment surgery is done under local anaesthesia. While pain may not be immediately felt, mild symptoms could be experienced at a later time.
Following Retinal Detachment surgery, it’s necessary to rest for a few days to weeks to ensure complete eye recovery. Consult your doctor regarding any dietary adjustments for optimal nutrition during the recovery period.
After Retinal Detachment surgery, follow these guidelines for a smoother recovery:
- Avoid heavy physical activities post-surgery.
- Position your head as instructed by your eye care provider.
- Wear protective glasses to shield your eyes from potential harm.
- Refrain from touching your eyes unnecessarily to prevent infection.
- Follow the prescribed eye drops for faster healing.
Other Diseases
Know more about other Eye Diseases
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy happens when high blood sugar levels damage the retinal blood vessels. In the early stages of Diabetic Retinopathy, symptoms may not be noticeable.
Retinopathy Prematurity
Retinopathy Prematurity (ROP) is an eye condition occurring in premature infants, where abnormal blood vessels grow in the retina, potentially resulting in blindness.